In mice, insulin injection reduces the level of anxiety by modulating the activity of this neuronal population. On the contrary, in mice fed a “high fat diet”, serotonin neurons become resistant to insulin and the beneficial behavioural effects of this hormone disappear.
This work offers interesting prospects, in particular the repositioning of oral antidiabetics – which improve insulin sensitivity – in the treatment of anxiety-depressive episodes.
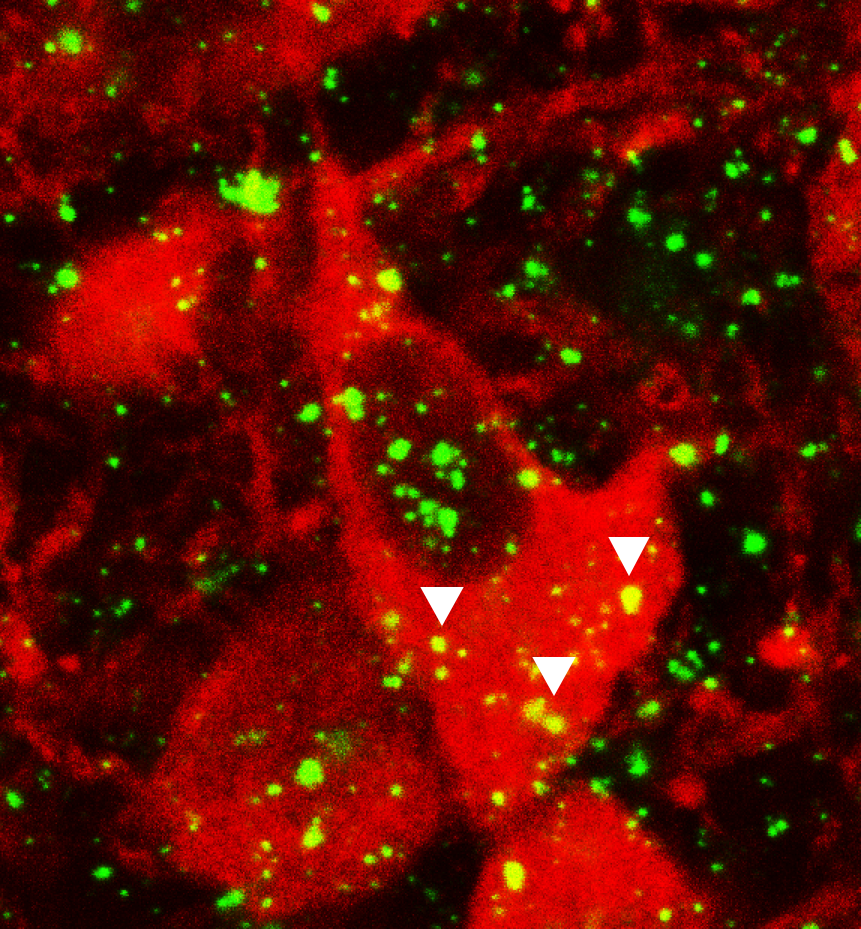
Extrait de la figure 1 de l’article de Martin, Bullich et al., 2022 (doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01812-3). Identification de la présence du récepteur à l’insuline sur les neurones sérotoninergiques du noyau dorsal du raphé. Images de microscopie confocales représentant les neurones sérotoninergiques en rouges (cellules TPH2 positives) et l’ARNm du récepteur à l’insuline (points verts) détecté par fluorescence après hybridation in situ. Le panel de droite (à fort grossissement) signale le co-marquage (triangles blancs) illustrant la présence du récepteur à l’insuline sur les neurones sérotoninergiques.
Reference
Martin H, Bullich S, Martinat M, Chataigner M, Di Miceli M, Simon V, Clark S, Butler J, Schell M, Chopra S, Chaouloff F, Kleinridders A, Cota D, De Deurwaerdere P, Pénicaud L, Layé S, Guiard BP, Fioramonti X
Insulin modulates emotional behavior through a serotonin-dependent mechanism.
Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 7. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01812-3
Contact
